

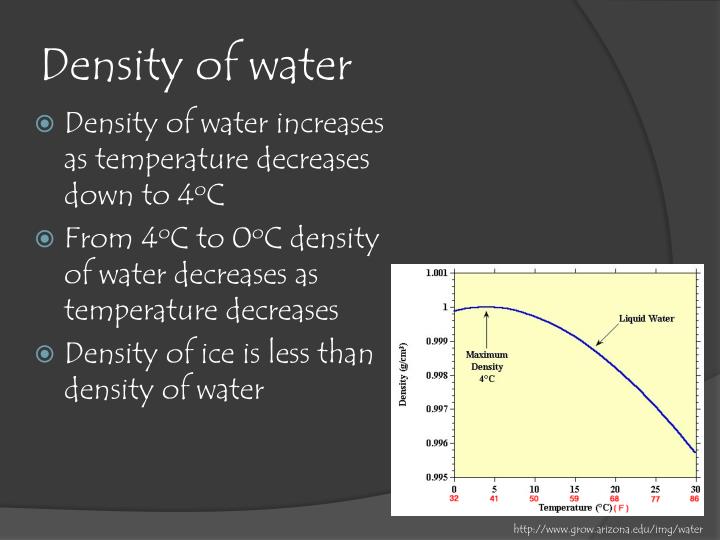
While you can round the density to 1 gram per milliliter, there are more precise values for you to use. The usual value used in calculations is 1 gram per milliliter (1 g/ml) or 1 gram per cubic centimeter (1 g/cm 3 ). See also other properties of Water at varying temperature and pressure: Boiling points at high pressure, Boiling points at vacuum pressure, Dynamic and kinematic viscosity, Enthalpy and entropy, Heat of vaporization, Ionization Constant, pK w, of normal and heavy water, Melting points at high pressure, Prandtl number, Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions, Saturation pressure, Specific gravity, Specific heat (heat capacity), Specific volume, Thermal conductivity, Thermal diffusivity and Vapour pressure at gas-liquid equilibrium.įor other substances, see density and specific weight o f acetone, air, ammonia, argon, benzene, butane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, ethane, ethanol, ethylene, helium, hydrogen, methane, methanol, nitrogen, oxygen, pentane, propane and toluene. The density of water is the weight of the water per its unit volume, which depends on the temperature of the water. See Water and Heavy Water for thermodynamic properties at standard condtions. The density of water depends on temperature and pressure as shown below: Temperature Choose the actual unit of temperature: Note! Temperature must be within the ranges 0-370 ☌, 32-700 ☏, 273-645 K and 492-1160 °R to get valid values. The output density is given as g/cm 3, kg/m 3, lb/ft 3, lb/gal(US liq) and sl/ft 3. The calculator below can be used to calculate the liquid water density at given temperatures. See more about the difference between mass and weight Online Water density Calculator The density of water is 1.940 sl/ft 3 at 39 ☏ (4 ☌), and the specific weight in Imperial units is In the Imperial system the mass unit is the slug, and is derived from the pound-force by defining it as the mass that will accelerate at 1 foot per square second when a 1 pound-force acts upon it:ġ = 1 * 1 and 1 = 1 /1 In the SI system, specific weight of water at 4☌ will be: G = acceleration due to gravity, units typically and value on Earth usually given as 9.80665 m/s 2 or 32.17405 ft/s 2 Specific weight is the ratio of the weight to the volume of a substance: Pure water has its highest density 1000 kg/m 3 or 1.940 slug/ft 3 at temperature 4☌ (=39.2☏). The lesser density means that ice contains lesser mass (quantity. At the same temperature of 0C, the density (mass per volume) of ice is 0.9187 grams per cubic centimeter (g cm -3 or g/cm 3) while that of liquid water is 0.9998 g cm -3 (Cohen et al. These electrostatic effect give rise to a shrinkage of the water.Density is the ratio of the mass to the volume of a substance: Density of Water: Water is less dense as ice than as a liquid, which affects plant life. In this way the field tends to disrupt hydrogen bonded structures in liquid water, and to compress the water molecules surrounding an ion.

The interaction of the electrostatic field of an ion with water tends to align the dipolar water molecules in the direction of the field. See this excerpt from a study on the volumetric effects due to ion-solvent interaction in aqueous electrolyte solutions: In this more ordered arrangement, the ions effectively fill the voids between the water molecules, and the volume of the water only increases slightly. The positive Hydrogen ends of the water molecules are attracted to the negatively charged Cl ions, and the positive oxygen ends are attracted to the positively charged Na ions. Because of the geometry of water molecules, they are essentially dipoles with “positive and a negative ends”.
/experiment-showing-relative-density-of-different-liquids-liquids-of-different-densities-will-sit-on-top-of-each-other-without-mixing-and-if-mixed-together-will-re-settle-into-layers-the-most-dense-liquid-lies-at-the-bottom-the-least-dense-at-the-t-57a768ac3df78cf459161869.jpg)
Interestingly, the dissolved salt does not increase the volume of the water by the volume of the added salt, and this is due to the charge of the Na and Cl ions and the H 2O molecules. When salt (sodium chloride or NaCl) dissolves in water, there is a significant increase in mass of the solution due to the relatively higher molecular mass of the dissolved ions Na (22 g/mol) and Cl (35.5g/mol) when compared to water or H 2O (20 g/mol).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
